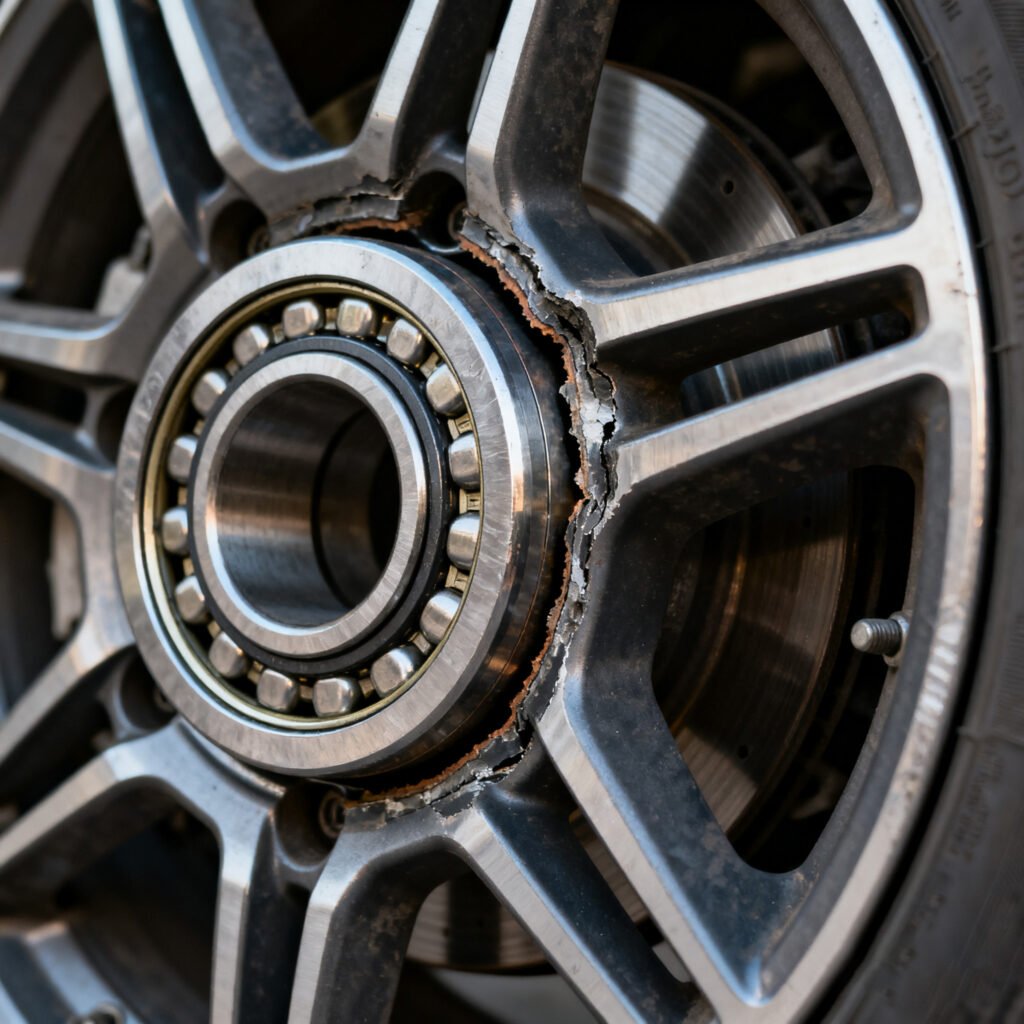
Your vehicle’s wheel bearings play a crucial role in safety, handling, and comfort. They allow the wheels to spin smoothly while carrying the full weight of the car. But when they begin to fail, the results can be noisy, uncomfortable, and even dangerous. Learning how to tell if your wheel bearing is bad is an essential skill for any driver or mechanic.
In this guide, we’ll cover what a wheel bearing does, the most common symptoms of failure, diagnostic methods, and why timely replacement is critical for safe driving.
What Does a Wheel Bearing Do?
A wheel bearing is a precision-engineered component located inside the wheel hub assembly. It reduces friction between the wheel and the axle, ensuring smooth rotation. Most modern vehicles use either Gen 1 (press-fit bearings), Gen 2 (hub and bearing combo), or Gen 3 (complete hub assembly) designs.
Regardless of the type, all wheel bearings serve the same purpose:
- Support the vehicle’s weight.
- Allow smooth wheel rotation.
- Maintain proper wheel alignment.
- Reduce friction and wear.
When a wheel bearing starts to fail, it can affect not only your comfort but also your ability to steer and stop safely.
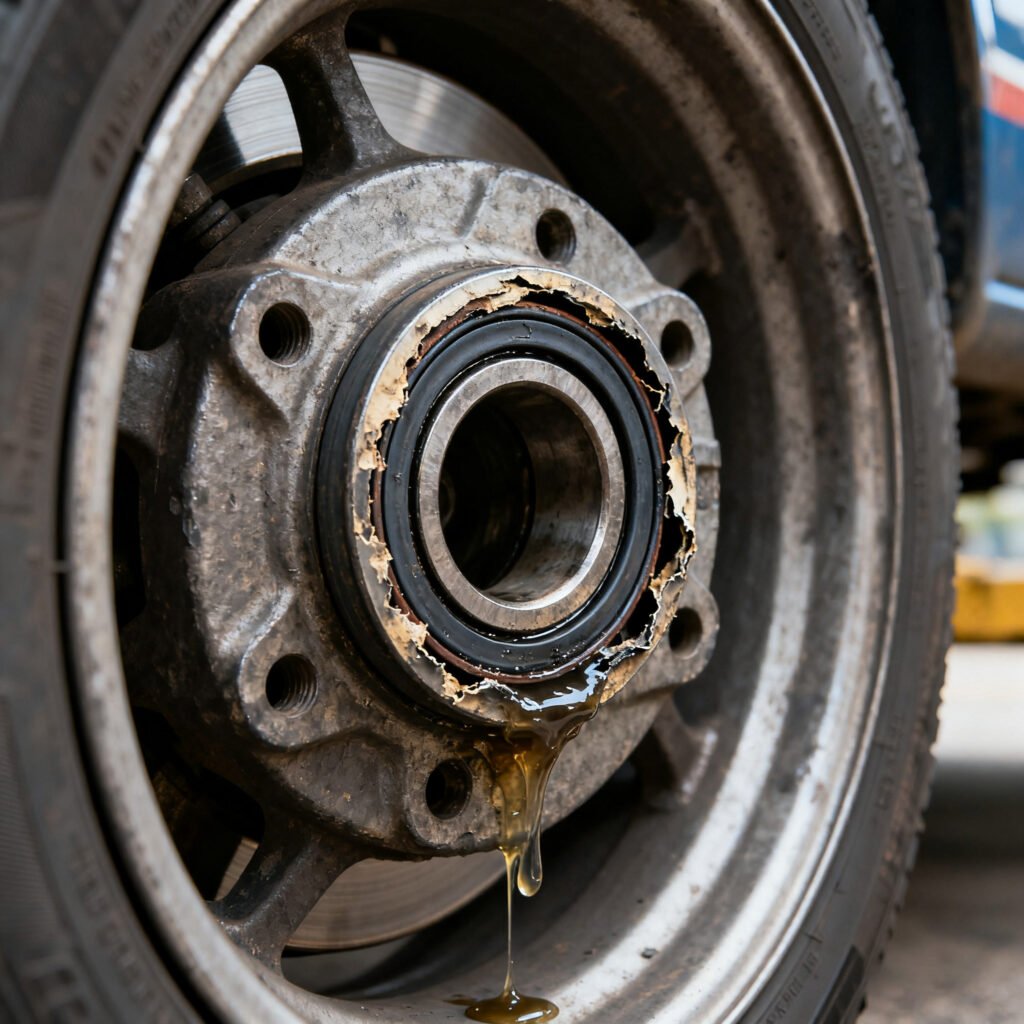

Symptoms of a Bad Wheel Bearing
Here are the most common signs that your wheel bearing may be going bad:
1. Grinding or Humming Noise
- One of the first and most noticeable symptoms is a grinding, humming, or roaring noise coming from the wheel area.
- The sound usually gets louder as the vehicle speeds up.
- It often changes when you turn left or right, depending on which bearing is failing.
2. Vibrations in the Steering Wheel
- A worn bearing can create noticeable vibrations, especially when driving at highway speeds.
- The steering wheel may feel shaky or unstable.
3. Uneven Tire Wear
- Damaged wheel bearings can cause the wheels to wobble slightly.
- This misalignment often leads to uneven or rapid tire wear.
4. ABS Warning Light
- In vehicles with ABS (anti-lock braking systems), some wheel bearings contain integrated ABS sensors.
- A failing bearing can trigger the ABS warning light on your dashboard.
5. Wheel Play or Looseness
- When the vehicle is lifted, you may notice excessive play when rocking the wheel side to side.
- This indicates looseness in the hub caused by a failing bearing.
6. Pulling to One Side While Braking
- If a bearing is badly worn, it can affect the brake rotor alignment.
- This may cause the car to pull to one side during braking.
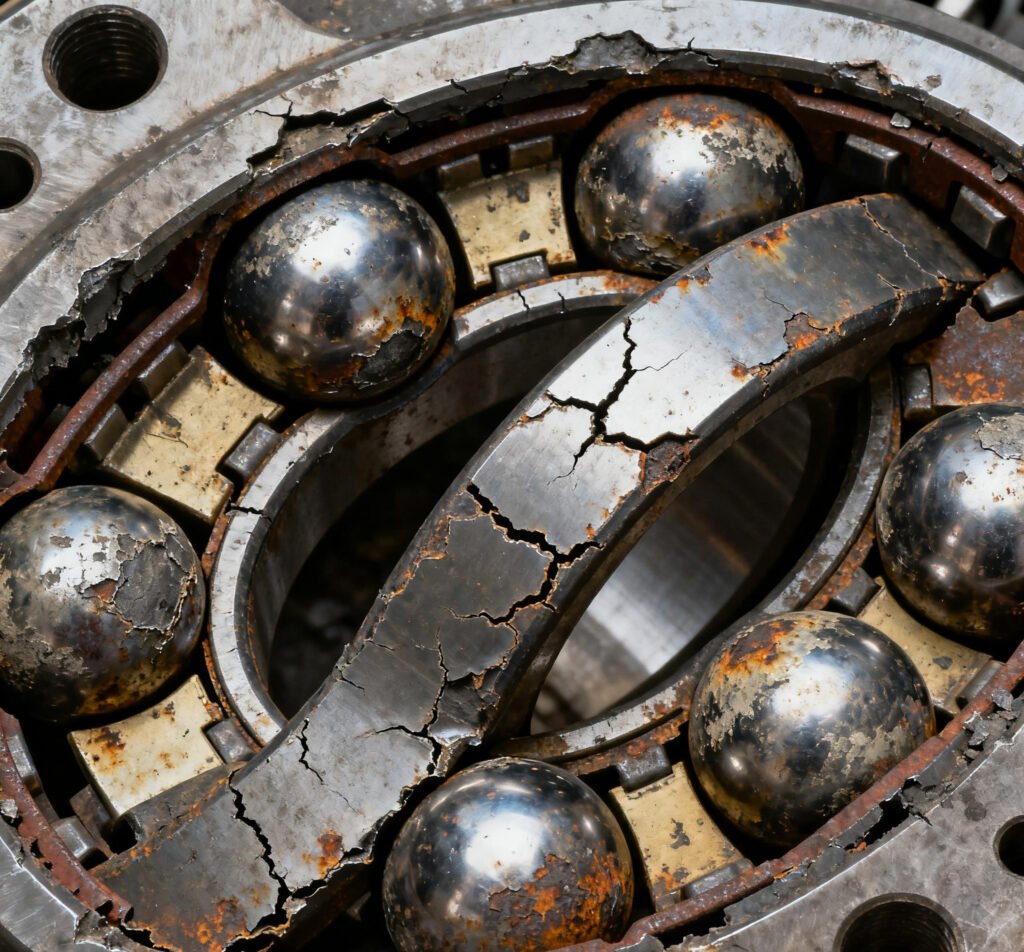

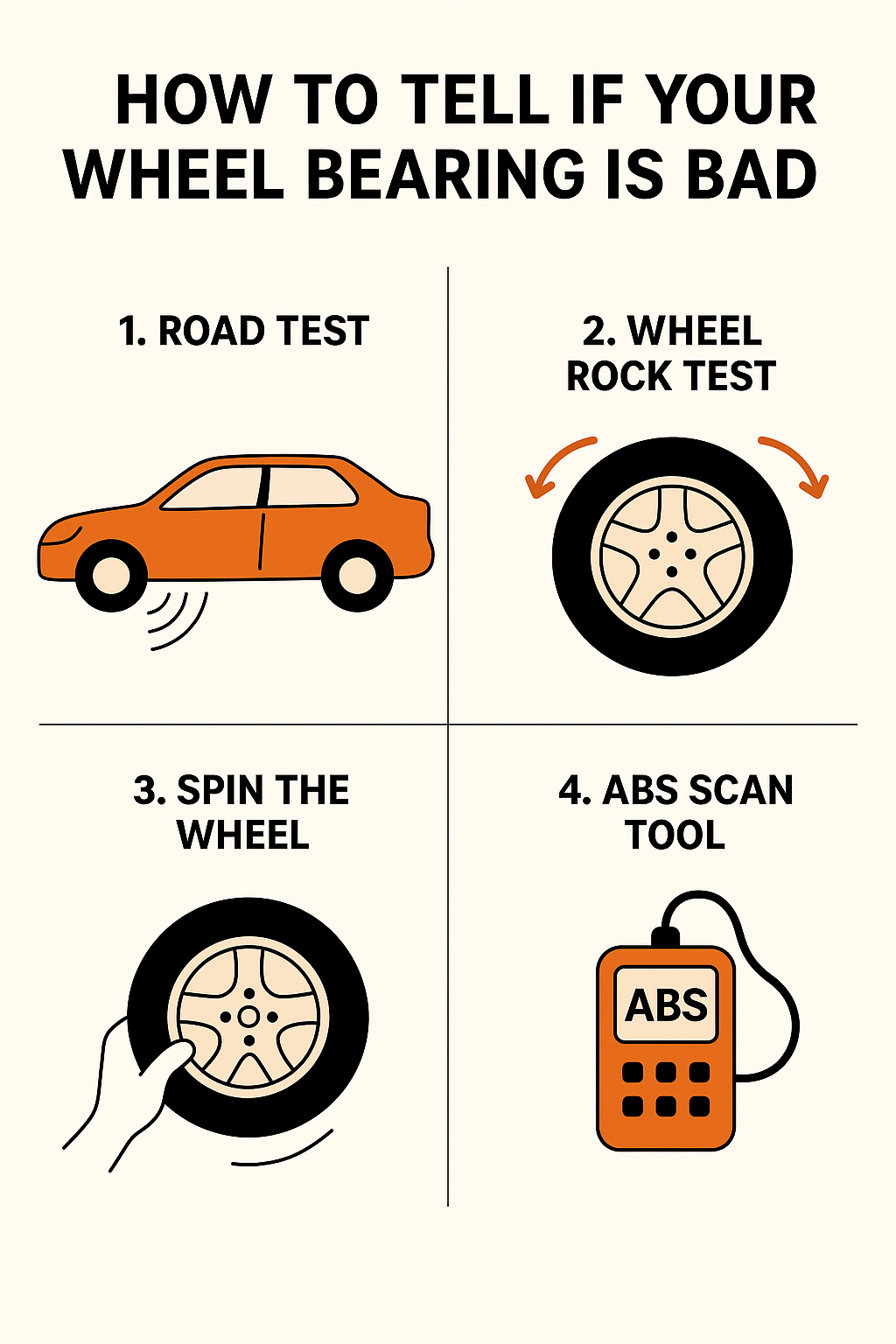
How to Diagnose a Bad Wheel Bearing
If you suspect your wheel bearing is failing, there are several ways to test it.
1. Road Test
- Drive at various speeds and listen carefully for humming or grinding noises.
- Pay attention to whether the noise changes when turning left or right.
2. Wheel Rock Test
- Safely lift the vehicle with a jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Grip the wheel at the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions.
- Rock the wheel back and forth. Excessive movement suggests bearing wear.
3. Spin the Wheel
- With the wheel lifted, spin it by hand.
- Listen for grinding, scraping, or roughness that indicates internal bearing damage.
4. ABS Scan Tool
- If your ABS light is on, use a diagnostic tool to check for ABS sensor errors.
- This may confirm if the bearing’s integrated sensor has failed.
How Long Do Wheel Bearings Last?
On average, a wheel bearing can last between 80,000 to 120,000 miles, depending on driving conditions. Rough roads, frequent heavy loads, or exposure to water and salt can reduce their lifespan significantly.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore a Bad Wheel Bearing
Driving with a bad wheel bearing is risky. Here’s why immediate action is important:
- Safety risk – A severely worn bearing can cause the wheel to lock or even detach in extreme cases.
- Brake performance issues – Damaged bearings affect rotor alignment, leading to longer stopping distances.
- Tire damage – Uneven wear shortens tire lifespan and costs more in replacements.
- Increased repair costs – Neglecting a failing bearing can damage the hub, spindle, or even suspension components.
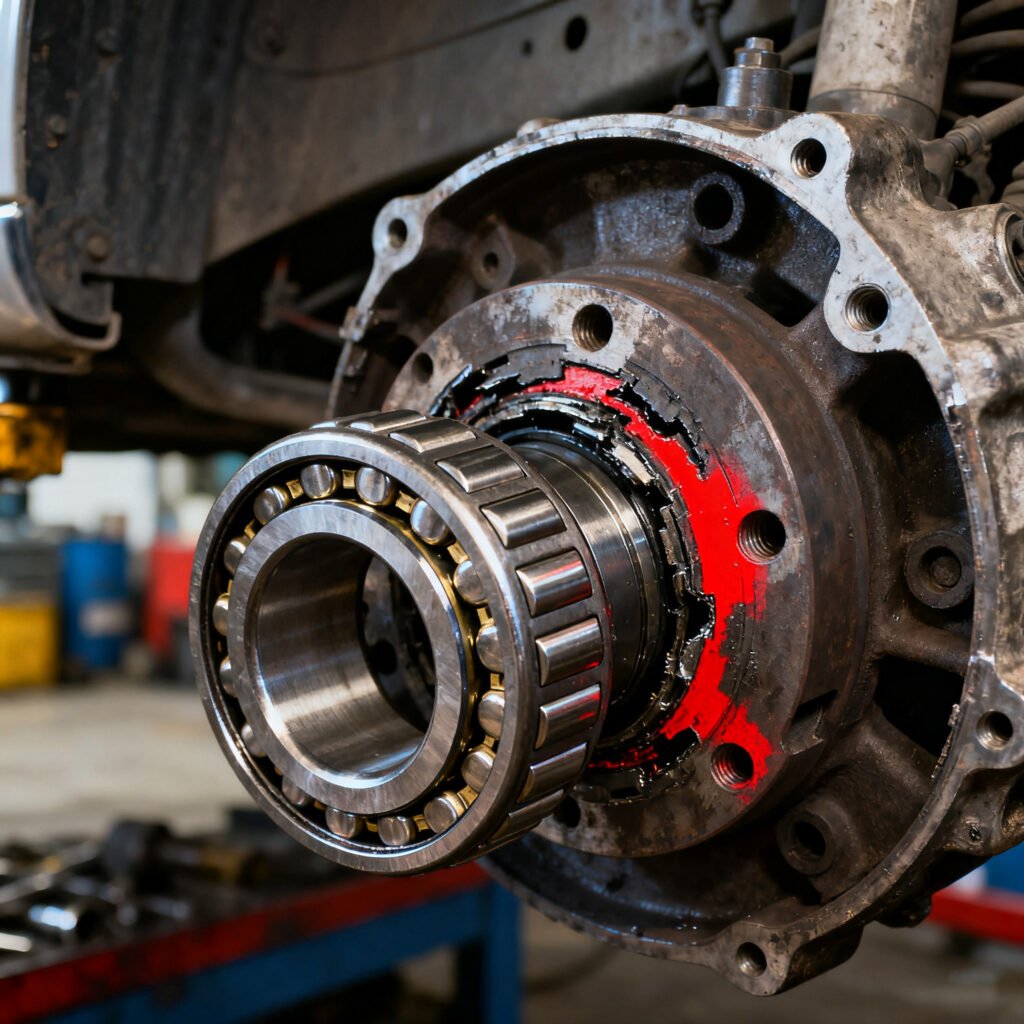

How to Prevent Wheel Bearing Failure
While no bearing lasts forever, proper care extends their life:
- Avoid deep water, mud, or harsh road conditions when possible.
- Rotate tires regularly to distribute wear evenly.
- Have bearings inspected during every brake service.
- Use OEM-quality bearings for replacements instead of cheap alternatives.
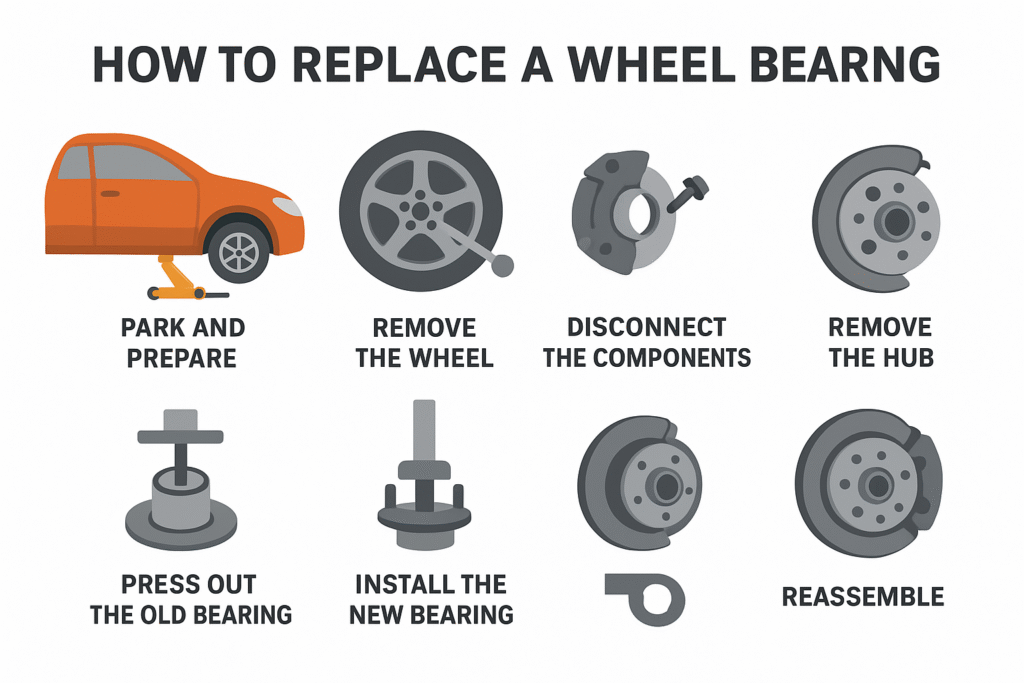
Wheel Bearing Replacement Options
If your bearing is bad, you have two choices:
- DIY Replacement – If you have mechanical skills and the right tools (especially a bearing press for Gen 1 bearings), you can replace it yourself.
- Professional Repair – For most drivers, visiting a mechanic is safer and ensures proper installation.
Cost depends on your vehicle:
- Parts: $50–$200 per bearing.
- Labor: $150–$300 per wheel at most shops.
Conclusion
Knowing how to tell if your wheel bearing is bad is vital for safe and reliable driving. Common warning signs include grinding noises, vibrations, uneven tire wear, ABS alerts, and wheel looseness. By diagnosing and replacing a failing bearing promptly, you prevent accidents, protect your tires, and ensure smooth driving performance.
If you suspect your wheel bearing is failing, don’t wait—inspect it immediately or visit a qualified mechanic. A healthy wheel bearing means a safer, quieter, and smoother ride.